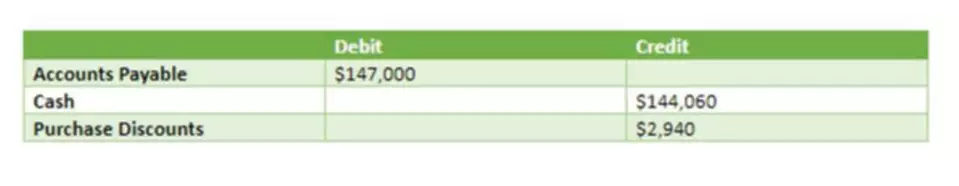
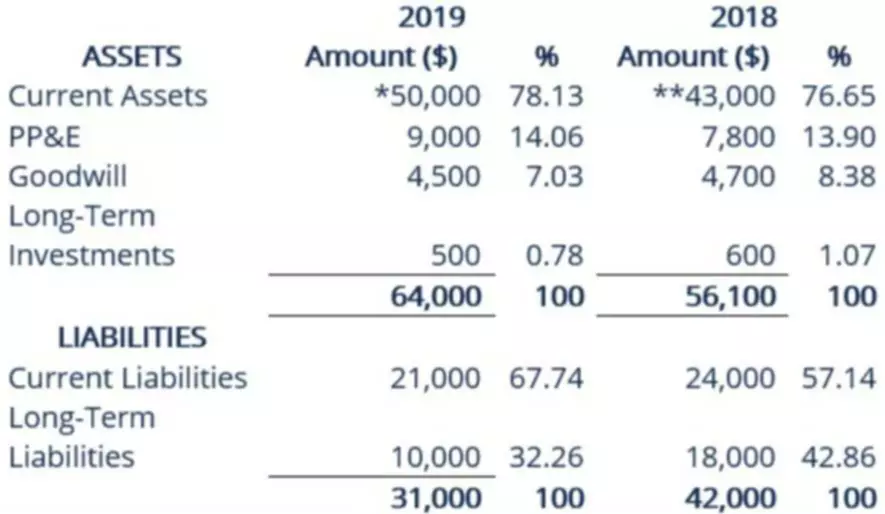
Content
We also reference original research from other reputable publishers where appropriate. You can learn more about the standards we follow in producing accurate, unbiased content in oureditorial policy. Kirsten Rohrs Schmitt is an accomplished professional editor, writer, proofreader, and fact-checker. She has expertise in finance, investing, real estate, and world history. Kirsten is also the founder and director of Your Best Edit; find her on LinkedIn and Facebook.
What Is Amortization? – Seeking Alpha
What Is Amortization?.
Posted: Wed, 09 Nov 2022 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The term declining balance depreciation refers to one of several methods of allocating the cost of an asset over its expected lifetime. The declining balance depreciation method is an accelerated approach to depreciation, and is based on the assumption an asset’s value declines at a greater rate in the early years of its serviceable life. With double declining balance depreciation, the 9% straight line rate is doubled to be 18%. Keep in mind that the 18% is multiplied by the asset’s book value at the beginning of the year. In the first year, the book value of the truck is the same as the truck’s original purchase price because the truck hasn’t been depreciated yet.
Using the 200% Double Declining Balance Depreciation Method
That’s the book value ($50,000) minus the depreciation ($9,000). Remember, every accounting term is going to stay a little hazy until you work through a couple examples. So, we’ll complete an example here—complete with full ten-year depreciation.
Because you’re subtracting a different amount every year, you can’t simply repeat the same calculation each year, as you can with the straight-line method. As mentioned earlier, this approach is particularly useful for property whose value will decrease rapidly after you acquire it. Acceleration means you are initially covering more “ground” over a shorter period of time. However, you still can’t depreciate an asset to a value less than its salvage value with the hard limit of zero.
Declining Balance Depreciation – Explained
Before joining FSB, Eric has worked as a freelance content writer with various digital marketing agencies in Australia, the United States, and the Philippines. Our ending book value is the beginning book value less depreciation expense. Now that we have a beginning value and DDB rate, we can fill up the 2022 depreciation https://www.bookstime.com/ expense column. If the beginning book value is equal with the salvage value, don’t apply the DDB rate. Instead, compute the difference between the beginning book value and salvage value to compute the depreciation expense. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers.
Under the straight-line depreciation method, the company would deduct $2,700 per year for 10 years–that is, $30,000 minus $3,000, divided by 10. The DDB depreciation method is easy to implement and track in most accounting software. If trying to calculate the reducing-balance method gets double declining balance method your mind tied up in knots, you can refer to the IRS calculation tables inPublication Additional Material. But if you’re not used to using them, these tables aren’t exactly a piece of cake, either. You’ll probably want to ask your accountant or tax preparer to perform this function.